Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition resulting in the loss of skin colour in patches. This leads to a noticeable contrast between affected and unaffected skin. It can affect anyone regardless of gender, age or ethnic background. At SkinAccess Clinics, we provide specialized care to manage vitiligo and help patients feel confident in their skin.
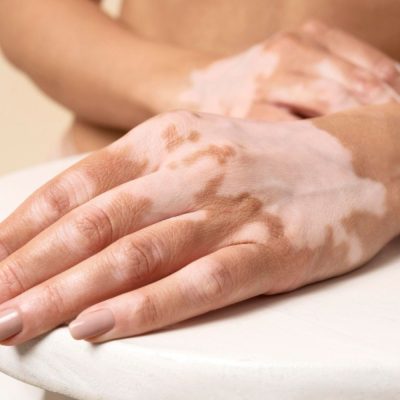

What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a condition in which the skin loses its pigment cells called melanocytes. This loss of pigmentation causes white patches to develop on the skin. It is known to affect any part of the body, including the skin, hair and even the inside of the mouth. Since vitiligo can vary significantly from person to person, it is impossible to predict the extent and rate of colour loss.
There are several types of vitiligo.
Generalized Vitiligo
This is the most common form of vertigo. Depigmented patches appear symmetrically on both sides of the body.
Segmental Vitiligo
Depigmentation occurs on only one side or part of the body and tends to progress for a few years before stopping.
Focal Vitiligo
This is characterized by one or a few scattered white patches in a localized area.
Universal Vitiligo
A rare form of vertigo where more than 80% of the body’s skin loses pigment.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
The primary symptom of vitiligo is the appearance of white or light-coloured patches on the skin. These patches are more noticeable in areas where the skin is exposed to the sun, like the face, hands, arms, feet and lips. Some other known symptoms include
1. Premature greying of the hair on the scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard
2. Loss of colour inside the mouth and nose (mucous membranes)
3. Change in colour of the retina (inner layer of the eyeball)
There is no physical discomfort such as pain or itching, but vitiligo can cause significant psychological and social impacts, particularly if it is present in visible areas of the body.
Causes of Vitiligo
The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully known; however, it is thought to be caused due to a combination of autoimmune, genetic and environmental factors.
Vitiligo is considered an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system attacks and destroys the melanocytes in the skin.
A family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Certain factors, such as sunburn, stress, or exposure to industrial chemicals, may trigger or exacerbate vitiligo in predisposed individuals.
Diagnosis of Vitiligo
A diagnosis is reached after a thorough physical examination and medical history review by a dermatologist. Ultraviolet light (UV) may be used to identify depigmented areas. At times, blood tests or a skin biopsy may be required to rule out other conditions or to check for associated autoimmune diseases.
Management and Treatment of Vitiligo
While there is no cure for vitiligo, there are several treatment options to help restore skin colour, slow or stop the progression of depigmentation and improve the appearance of the affected areas. At SkinAccess Clinics, we offer a range of individualized treatments tailored to suit each patient’s needs
➥ Topical Treatments: Creams may be prescribed to help restore pigmentation in small areas of the skin. These treatments are most effective in the early stages.
➥ Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Melanocyte production is stimulated to help restore skin colour. This is done by Narrowband UVB Phototherapy which is one of the most common and effective treatments for vitiligo.
➥ Excimer Laser Therapy: This is a more targeted form of phototherapy used for smaller areas and can help to re-pigment specific patches of skin.
➥ Vitiligo Surgery: Skin grafting and melanocyte transplantation are options for patients with stable vitiligo. However, surgery is always the last option and is only recommended to patients who do not respond to other forms of treatment.
➥ Depigmentation: In cases of extensive or Universal Vitiligo. Depigmenting may be considered, to create a more uniform appearance.
