Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Characterized by red, scaly patches, it can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life. At SkinAccess Clinics, we provide comprehensive, personalized care to help manage and treat psoriasis effectively.
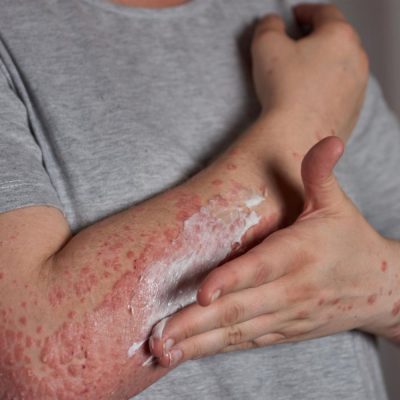
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that speeds up the life cycle of skin cells causing cells to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface, forming scales and red patches. These patches can be painful, itchy and at times may even bleed. Psoriasis is a chronic (long-lasting) condition that can fluctuate between periods of remission and flare-ups.
There are several types of psoriasis.
Plaque Psoriasis
This is the most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales.
Guttate Psoriasis
This presents as small drop-shaped sores, usually triggered by a bacterial infection like strep throat.
Inverse Psoriasis
This usually appears in body folds such as the groin or armpit and presents in the form of red, shiny lesions.
Pustular Psoriasis
Typically found on the hands and feet, this presents as white pustules surrounded by red skin.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
This is the most severe form which can even be life-threatening. It covers large areas of the body with a red, peeling rash.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common signs include
1. Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
2. Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
3. Itching, burning, or soreness
4. Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
5. Swollen and stiff joints (associated with psoriatic arthritis)
Symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some individuals may experience only minor irritation while others may suffer from extensive, painful outbreaks. Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees and lower back.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact causative factor of psoriasis has not yet been fully understood, however, it is believed to be a combination of the immune system, genetic and environmental factors.
Psoriasis tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid cell turnover and inflammation.
Certain factors can trigger or worsen psoriasis, including infections, certain medications, stress and skin injuries. Even environmental factors like cold weather have been known to be triggers.
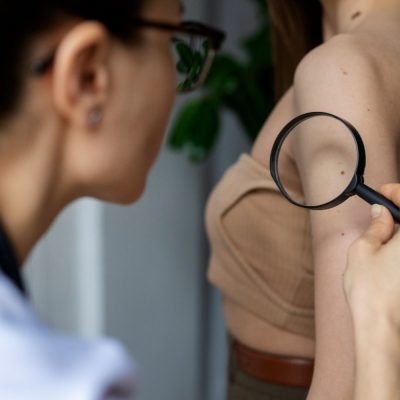
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
A diagnosis typically involves a physical examination of the affected areas by a dermatologist. At times, a skin biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Management and Treatment of Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are a variety of treatment options available to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. An individualized and personalized treatment plan is developed depending on the type and severity of the condition. Regular monitoring is extremely important as the doctor needs to assess the patient’s response to the treatment and may need to adjust medications accordingly. At SkinAccess Clinics, we offer a full range of effective therapies
➥ Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments which help reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell production, and remove scales are prescribed. These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, and salicylic acid.
➥ Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. UVB phototherapy and excimer laser therapy are common options.
➥ Systemic Medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed. These include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics that target specific parts of the immune system.
➥ Lifestyle and Skincare Recommendations: Patients are advised on how to manage triggers, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and use gentle skincare products to prevent flare-ups.
